How Germs Spread
Washing hands can keep you healthy and prevent the spread of respiratory and diarrheal infections from one person to the next. Germs can spread from other people or surfaces when you:
- Touch your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands
- Prepare or eat food and drinks with unwashed hands
- Touch a contaminated surface or objects
- Blow your nose, cough, or sneeze into hands and then touch other people’s hands or common objects
Key Times to Wash Hands
You can help yourself and your loved ones stay healthy by washing your hands often, especially during these key times when you are likely to get and spread germs:

- Before, during, and after preparing food
- Before and after eating food
- Before and after caring for someone at home who is sick
- Before and after treating a cut or wound
- After using the toilet
- After changing diapers or cleaning up a child who has used the toilet
- After blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing
- After touching an animal, animal feed, or animal waste
- After handling pet food or pet treats
- After touching garbage
The guidance for the list of key times to wash hands was developed based on data from several. There can also be other times when it is important to wash hands.
To prevent the spread of germs during the COVID-19 pandemic, you should also wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or use a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol to clean hands BEFORE and AFTER:
- Touching your eyes, nose, or mouth
- Touching your mask
- Entering and leaving a public place
- Touching an item or surface that may be frequently touched by other people, such as door handles, tables, gas pumps, shopping carts, or electronic cashier registers/screens
The UK government guidelines for washing hands.
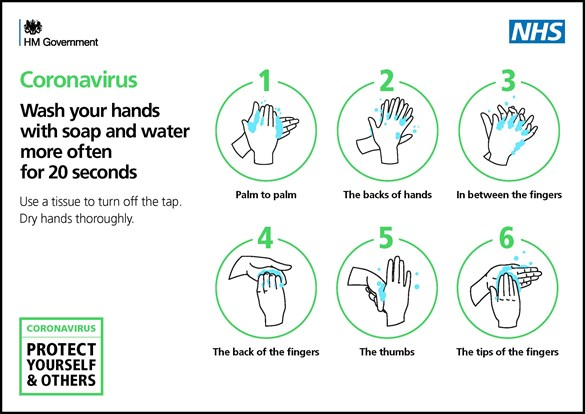
Here is the UK, the government’s recent best practice guidelines and advice suggest that we would like to emphases the importance of washing your hands more often, especially:
- When you get to work or arrive back home.
- After you blow your nose, cough or sneeze.
- Before you eat or handle food. You should wash your hands for 20 seconds, using soap and water or hand sanitizer.
If you do not have access to running water and soap, use hand sanitiser, but ensure that you wash your hands once you are able to.
You should also cough or sneeze into tissues before binning them.
The CDC (Center for disease control) advice on hand washing.
Washing your hands is easy, and it’s one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of germs. Clean hands can stop germs from spreading from one person to another and throughout an entire community—from your home and workplace to childcare facilities and hospitals.
Follow these five steps every time.

- Wet your hands with clean, running water (warm or cold), turn off the tap, and apply soap.
- Lather your hands by rubbing them together with the soap. Lather the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
- Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds. Need a timer? Hum the “Happy Birthday” song from beginning to end twice.
- Rinse your hands well under clean, running water.
- Dry your hands using a clean towel or air dry them.
What Hand Sanitiser is most effective, and when to use it.
In situations where you do not have access to soap, water and washing facilities, the CDC recommends the use of alcohol-based hand sanitizer containing at least 60% ethyl alcohol. This can be listed in the ingredients list as; ethanol, ethyl alcohol, isopropanol or 2-propanol. As of November 2020, the CDC suggested what to avoid while purchasing hand sanitizer. The CDC suggest these 4 simple criteria when choosing hand sanitizer.
- Hand sanitizers that contain less than 60 percent alcohol is less effective
- Awareness of hand sanitizers listed on the FDA’s Hand Sanitizer Do-Not-Use List
- Hand sanitizers that are labelled “alcohol-free”
- Hand sanitizers packaged in a container that resembles a food or beverage container
Caution! Swallowing alcohol-based hand sanitizers can cause alcohol poisoning if more than a couple of mouthfuls are swallowed. Keep it out of reach of young children and supervise their use.


Click Here to see more good practices regarding Covid-19 saftey measures.
